# SQL Relations
To refer from one table to the other. For Example:
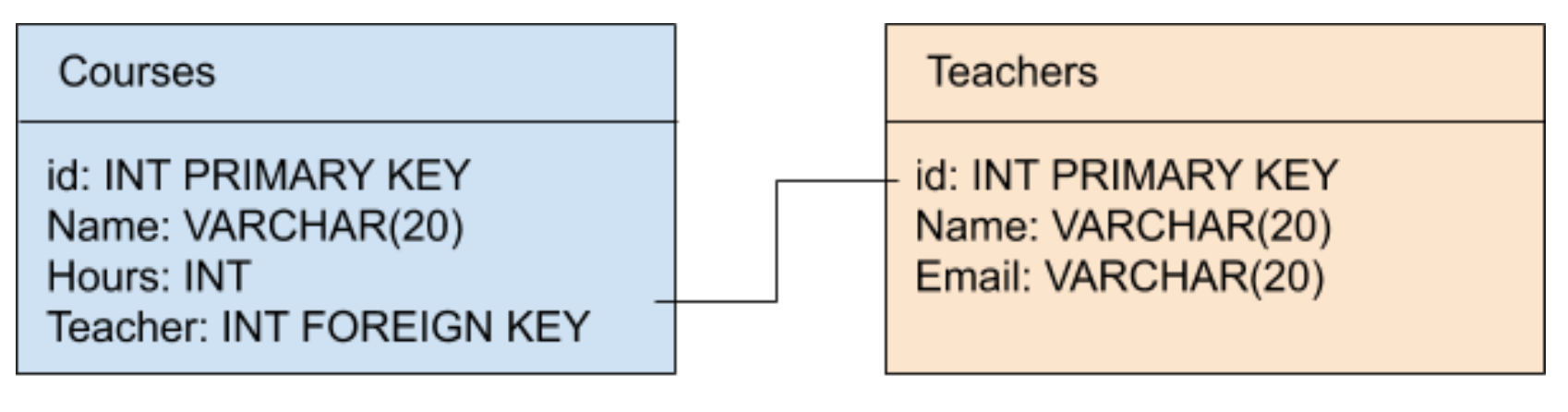
A table “Teachers” and a table “Courses”. In the table “Courses” you have a column called “Teacher” where you want to refer to an entry in the table “Teachers”.
# Foreign keys
(point to other table)
https://www.w3schools.com/sql/sql_foreignkey.asp)
CREATE TABLE orders (
id INT NOT NULL,
oder_number INT,
customer_id INT,
product_id INT,
PRIMARY KEY (id),
FOREIGN KEY (customer_id) REFERENCES customers(id),
FOREIGN KEY (product_id) REFERENCES products(id),
)
Tutorial on foreign keys - MariaDB (opens new window)
A foreign key refers to a column in a different table.
In our example, we have a table “Teachers” and a table “Courses”. In "courses", we have a column called “Teacher”, which refers to the “Teacher” table.
Use SHOW CREATE TABLE to see how it was created: CONSTRAINT
+---------+--------------------------------------
| Table | Create Table
+---------+--------------------------------------
| Courses | CREATE TABLE `Courses` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`hours` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`teacher` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `teacher` (`teacher`),
CONSTRAINT `teacher` FOREIGN KEY (`teacher`) REFERENCES `Teachers` (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 |
+---------+--------------------------------------
like this:
KEY <key_name> (<column_name>), # key_name: you can choose a name
CONSTRAINT <constraint_name> # constraint_name: you can choose a name
FOREIGN KEY (<column_name>) # specify column in the table
REFERENCES <foreign_table>(<foreign_column>)
# table and column) from the referenced table
# One-to-Many Relationships
The example above is a one-to-many relationship.
A teacher can teach multiple courses, but a course can only have one teacher.
- you do this by creating a foreign key in the table of the entity of the “one” side.
- put the reference in the table that can only have one reference to the other
- In our example, that’s the Courses table, because a course can only have one teacher
⚠ Important: Always put the foreign key into the table of the “one” side of the one-to-many relationship. It does not work on the “many” side.
# Many-to-Many Relationships
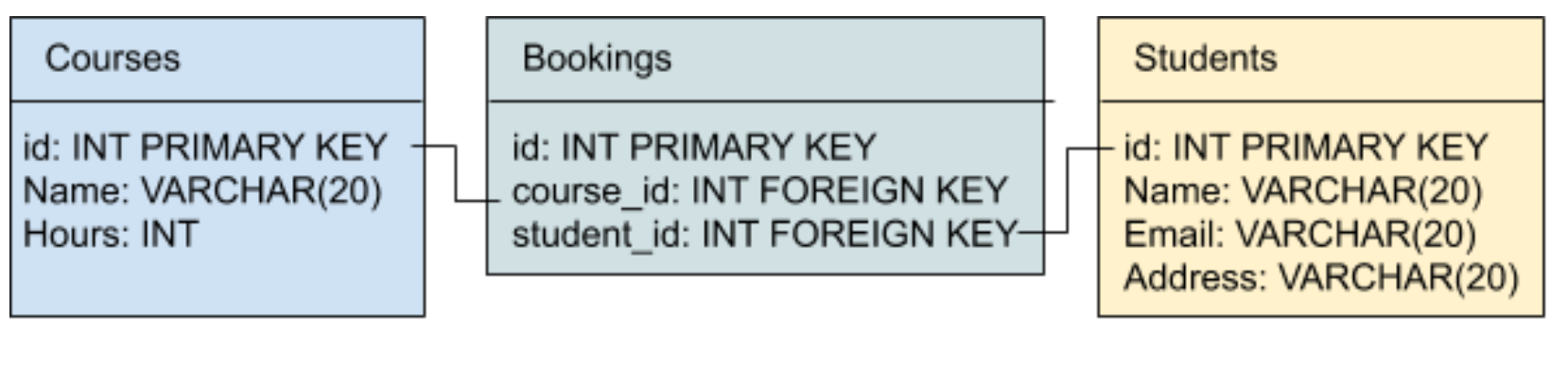
For example, if you have a table “Courses” and a table “Students”, you want to connect these two tables in some way that a student can take many courses, and a course can have many students.
This is done by creating a third table that represents the relationship.