# HTML-Basics
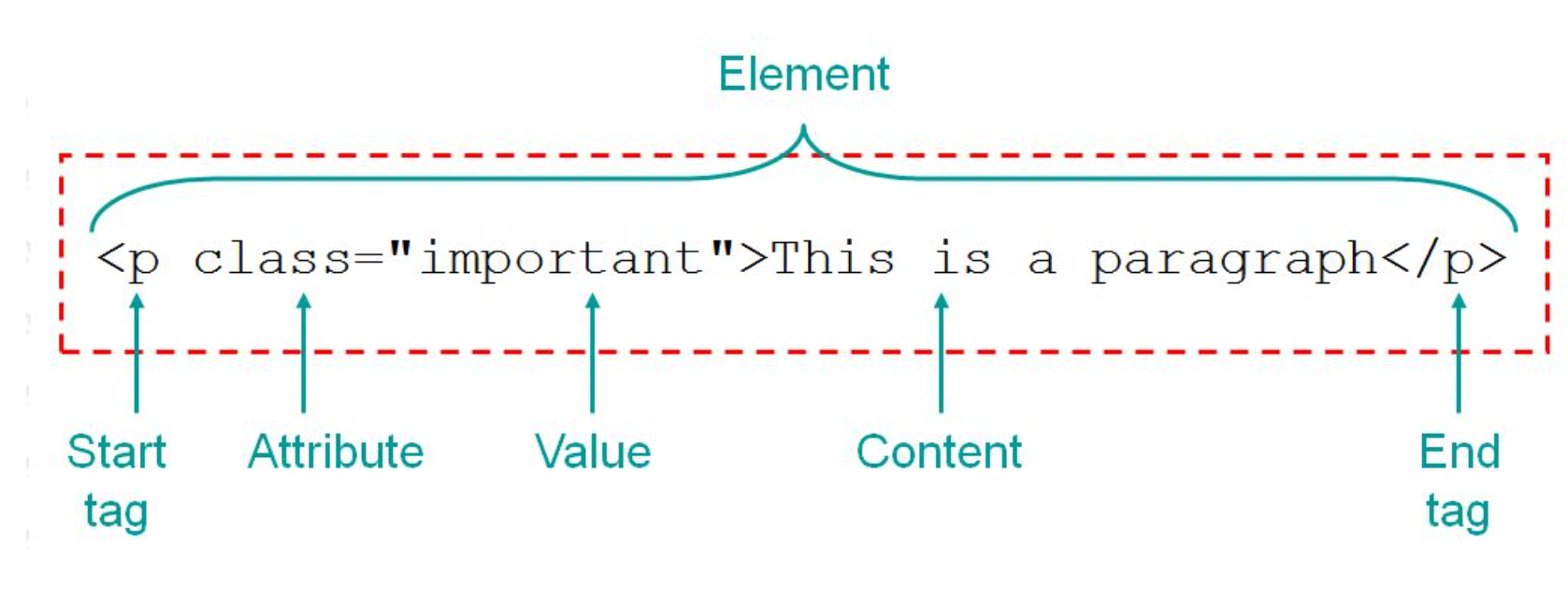
# HTML Syntax
# Head
<head>
<title>Hamburg Coding School</title>
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<meta name="last-modified" content="Mon, 06 Jan 2020 16:23:39 CET" />
<meta name="description" content="Programmier-Kurse, die Spaß machen." />
<meta property="og:title" content="Hamburg Coding School" />
<meta
property="og:description"
content="Programmier-Kurse, die Spaß machen."
/>
<meta
property="og:image"
content="https://hamburgcodingschool.com/class-201811.jpg"
/>
<meta name="twitter:card" content="summary_large_image" />
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1"
/>
<link
rel="stylesheet"
href="https://hamburgcodingschool.com/css/codingschool.css"
/>
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="/favicon.png" />
<style>
h1 {
color: red;
}
p {
color: blue;
}
</style>
<script>
window.onload = function() {
if (window.matchMedia('(max-width: 48em)').matches) {
location.hash = '#content-start';
}
};
</script>
</head>
<title> | Contains the title of the website = the name that is displayed in the browser tab. |
<meta> | Includes meta information that is used for e.g. displaying snippets in search results or link previews in social media. |
<link> | Includes CSS into the document, or loads the favicon (shortcut icon) |
<style> | Defines local CSS styles. |
<script> | Defines local JavaScript |
# Metadata
The <meta> tags contain metadata: Data that is not displayed on the page, but is machine parsable. Meta elements typically contain information about:
- page description
- keywords
- author of the document
- last modified or
- thumbnail image
Metadata is mostly used by search engines or by social media to display snippets with title, description and a thumbnail image.
# Viewport
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
# Link
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/styles.css" type="text/css" />
</head>
# FavIcon
Fav Icon dem Titel hinzufügen:
<link rel="icon" href="images/icon.png" type="image/png" />
# Anchor Links
<a href="https://hamburgcodinschool.com">Where i learned HTML</a>
There are 3 types of destinations you can define:
- anchor targets, to navigate within the same page
- relative URLs, usually to navigate within the same website
- absolute URLs, usually to navigate to another website
You can also use additional attributes besides a and href:
specify the relationship between the current and linked document with the
relattributespecify where to open the linked document with the
targetattribute
# Download-Link
<a href="/assets/file.pdf" download>Download PDF... </a>
# Text Formatting Tags
HTML brings some tags for structuring and formatting your text.
| Tag | |
|---|---|
<p> | A paragraph. Adds space before and after the text. The most used HTML element - the default block-level element |
<br> | A line break. Single tag without closing tag. |
<div> | A box. Unlike <p>, <div> doesn’t add space before or after the text. |
<h1> | A headline. You can choose from <h1> (largest) to <h6> (smallest). |
<b> | Makes the text bold. Inline tag: does not break the text. |
<i> | Makes the text italic. Inline tag: does not break the text. |
<u> | Underlines the text. Inline tag: does not break the text. |
<small> | Makes the text smaller. Inline tag: does not break the text. |
- HTML Text Formatting - w3schools (opens new window)
- b - MDN (opens new window)
- Simple HTML Guide - Cheatsheet (opens new window)
# HTML File-Paths
| Path | |
|---|---|
<img src="picture.jpg"> | The "picture.jpg" file is located in the same folder as the current page |
<img src="images/picture.jpg"> | The "picture.jpg" file is located in the images folder in the current folder |
<img src="/images/picture.jpg"> | The "picture.jpg" file is located in the images folder at the root of the current web |
<img src="../picture.jpg"> | The "picture.jpg" file is located in the folder one level up from the current folder |
./resources/css/index.css | |
./ | same folder |
It is best practice to use relative file paths (if possible).
# Entities
| Entity | Result |
|---|---|
> | > |
< | < |
& | & |
" | " |
' | ' |
€ | € |
© | © |
| non breaking Space |
# Images
<img src="path/to/picture.jpg" alt="funny cat picture" />
Most retina displays use double the amount of pixels, so it is a good rule of thumb to make your images double the size of how you want them to include in your HTML document. In the example of the 500x500 pixels profile picture, you need to prepare the image so that it is 1000x1000 pixels wide
| jpg | compressed image |
| png | background kann sich bewegen/verändern? -> braucht mehr Speicher |
| gif | bewegen sich |
| svg | Scalable Vector Graphics: Vector |
# Lists
<li> | List Item |
<ul> </ul> | Unordered List |
<ul style="list-style-type:*circle*"> | disk (default) / circle / square / none |
<ol type=? start=?> </ol> | Ordered List |
| type="1" | 1. 2. 3. |
| type="A" | A. B. C. |
| type="a" | a. b. c. |
| type="I" | I. II. III. |
| type="i" | i. ii. iii. |
# Tables
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
<table> | Tabelle |
<tr> | Table Row - Zeile |
<td> | Table Data - Zelle |
<th> | Table Header - Überschrift |
<th scope="row/col"> | Ausrichtung der Überschrift Zeile/Spalte |
<tg colspan="?"> | Inhalt über mehrere Zellen verbinden |
<tg rowspan="?"> | Inhalt über mehrere Zeilen verbinden |
<thead> </thead> | Table Head - eigener Abschnitt für die Überschrift |
<tfoot> </tfoot> | Table Foot - eigener Abschnitt für die Fusszeile |
<tbody> </tbody> | Table Body - eigener Abschnitt für den Body |
- Tables - w3schools (opens new window)
- Tables - MDN (opens new window)
- A Complete Guide to the Table Element - CSS Tricks (opens new window)
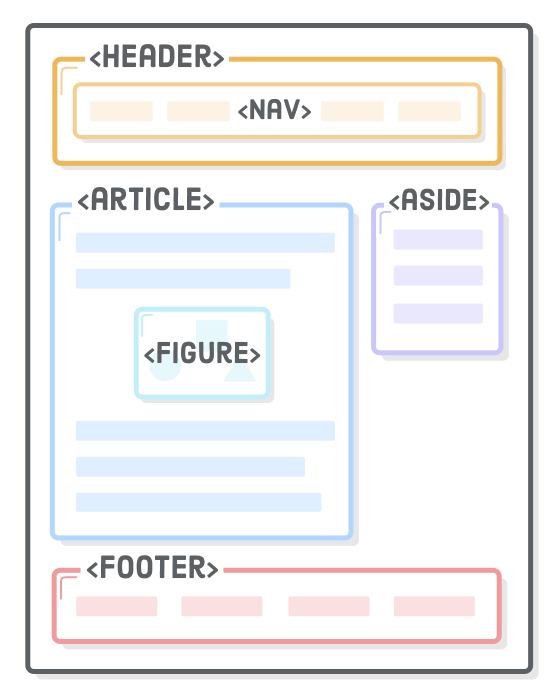
# SemanticHTML
Structure the Code for better Readability and SEO:
eg. <header> <footer> <nav> <main> etc.
- Semantic Elements - w3schools (opens new window)
- Semantic HTML - codecademy (opens new window)
- Semantic HTML - interneting is hard (opens new window)
Here’s what a typical webpage could include:
<header>as the first element of the page, that can include the logo and the tagline.<nav>as a list of links that go to the different pages of the website.<h1>as the title of the page.<article>as the main content of the page, like a blog post.<footer>as the last element of the page, located at the bottom.
# Audio-Video
<audio>, <video> and <embed> (embed is self-closing):
<!-- Audio Tag -->
<audio src="koreanhiphop.mp3" controls autoplay></audio>
<!-- Video Tag -->
<video src="4kvideo.mp4">video not supported</video>
<!-- Embed Tag -->
<embed src="babyyoda.gif" />
# Data-Attribute
The data-* attribute is used to store custom data private to the page or application.