# Sequelize
- instead of writing SQL queries manually, you can use ORMs like Sequelize -> work with native JS object
- allows to define models and interact with teh db through them
- you can also easily setup relations ('Associations') and interact with the models through them ('magic methods')
https://sequelize.org/master/ (opens new window)
npm i sequelize
also needs mysql2-package
# connect to the database
in /utils/database.js - create the pool:
const Sequelize = require('sequelize');
const sequelize = new Sequelize('DB_NAME', 'USER', 'PASSWORD', {
dialect: 'mysql',
host: 'localhost',
});
module.exports = sequelize;
# create a model
in /models/product.js
const Sequelize = require('sequelize');
const sequelize = require('../util/database.js');
const Product = sequelize.define('product', {
id: {
type: Sequelize.INTEGER,
autoIncrement: true,
allowNull: false,
primaryKey: true,
},
title: Sequelize.STRING,
price: {
type: Sequelize.DOUBLE,
allowNull: false,
},
imageUrl: {
type: Sequelize.STRING,
allowNull: false,
},
description: {
type: Sequelize.STRING,
allowNull: false,
},
});
module.exports = Product;
in app.js
const sequelize = require('./util/database.js');
// ...
sequelize
.sync()
.then((result) => {
// console.log(result);
console.log('running with db');
app.listen(3000);
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log(err);
});
sync() creates/syns tables for all models
-› table name automatically gehts pluralized
model: Product -> table: products
# Insert data
Product.create() creates a record, build() creates it but does't save it to the database
exports.postAddProduct = (req, res, next) => {
const title = req.body.title;
const imageUrl = req.body.imageUrl;
const price = req.body.price;
const description = req.body.description;
Product.create({
title: title,
price: price,
imageUrl: imageUrl,
description: description,
})
.then((result) => {
console.log('>>>created product');
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log(err);
});
};
With Sequelize v5,
findById()was replaced byfindByPk().
# get data
Model.findAll()
exports.getIndex = (req, res, next) => {
Product.findAll()
.then((products) => {
res.render('shop/index', {
prods: products,
pageTitle: 'Shop',
path: '/',
});
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log(err);
});
};
get prodct by id:
exports.getProduct = (req, res, next) => {
const prodId = req.params.productId;
Product.findByPk(prodId)
.then((product) => {
console.log(product);
res.render('shop/product-detail', {
product: product,
pageTitle: product.title,
path: '/products',
});
})
.catch((err) => console.log(err));
};
alternative using findAll():
https://sequelize.org/master/manual/model-querying-basics.html (opens new window)
exports.getProduct = (req, res, next) => {
const prodId = req.params.productId;
Product.findAll({
where: {
id: prodId,
},
})
.then((products) => {
res.render('shop/product-detail', {
product: products[0],
pageTitle: products[0].title,
path: '/products',
});
})
.catch((err) => console.log(err));
};
# Change/Update data
Model.save()
if the product doesn't exist, a new one will be generated, otherwise, the old one will be updated
exports.postEditProduct = (req, res, next) => {
const prodId = req.body.productId;
const updatedTitle = req.body.title;
const updatedPrice = req.body.price;
const updatedImageUrl = req.body.imageUrl;
const updatedDescription = req.body.description;
Product.findByPk(prodId)
.then((product) => {
product.title = updatedTitle;
product.price = updatedPrice;
product.description = updatedDescription;
product.imageUrl = updatedImageUrl;
return product.save();
})
.then((result) => {
console.log('>>>updated product');
res.redirect('/admin/products');
})
.catch((err) => console.log(err));
};
returning the last function of the fist
.then-block as a promise:
.catchhandles errors for both!!
# Delete Data
Model.destroy({OPTIONS})
or use findByPk
exports.postDeleteProduct = (req, res, next) => {
const prodId = req.body.productId;
Product.findByPk(prodId)
.then((product) => {
return product.destroy();
})
.then((result) => {
console.log('>>>destryoed product');
res.redirect('/admin/products');
})
.catch((err) => console.log(err));
};
# Associations / Relations
https://sequelize.org/master/manual/assocs.html
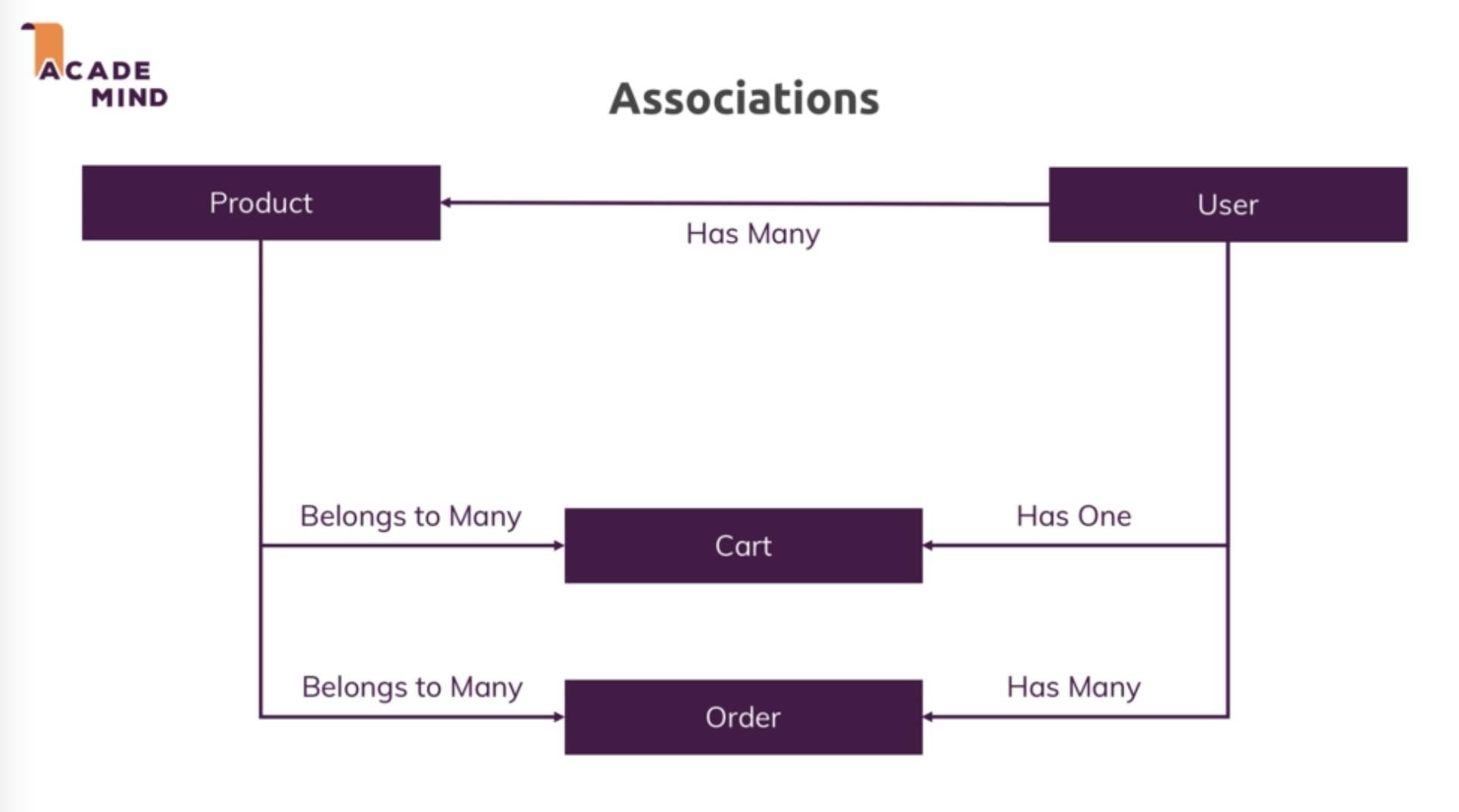
# One-to-many relationship
in app.js
const sequelize = require('./util/database.js');
const Product = require('./models/product')
const User = require('./models/user')
// ...
Product.belongsTo(User, {})
(User created the Product)
onDelete: 'CASCADE'
-> Product will also be deleted, when the User is deleted
you can define both directions:
Product.belongsTo(User, { constraints: true, onDelete: 'CASCADE' });
User.hasMany(Product)
to make sure that changes are applied (you don't use this in producition):
sequelize
.sync({ force: true })
-> ovewrites the tables
-> product get's a field: foreignKey : userId -> references the user
Promise.resolve(data) sends a promise that imediately resolves to the data
but it is not really needed in a then-block
you can always add a new property to the req, like:
app.use((req, res, next) => {
User.findByPk(1)
.then((user) => {
req.user = user;
next();
})
.catch((err) => console.log(err));
});
-> then you have access everywhere to req.user
you can even:
-> sequelize add special methods with the assiciations
since user.hasMany(Product)
-> there is a method user.createProduct()
exports.postAddProduct = (req, res, next) => {
const title = req.body.title;
const imageUrl = req.body.imageUrl;
const price = req.body.price;
const description = req.body.description;
req.user
.createProduct({
title: title,
price: price,
imageUrl: imageUrl,
description: description,
})
.then((result) => {
console.log('>>>created product');
res.redirect('/admin/products');
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log(err);
});
};
find only products made by that user
req.user
.getProducts({ where: { id: prodId } })
.then((products) => {
(you get an array of the results)
# One-to-many and Many-to-many realtionships
Product.belongsTo(User, { constraints: true, onDelete: 'CASCADE' });
User.hasMany(Product);
User.hasOne(Cart);
Cart.belongsTo(User);
Cart.belongsToMany(Product, { through: CartItem });
Product.belongsToMany(Cart, { through: CartItem });
magic function:
user.createCart();
delete item:
product.cartItem().destroy();
...